| Command's Purpose | MS-DOS | Linux | Basic Linux Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copies files | copy | cp | cp thisfile.txt /home/thisdirectory |
| Moves files | move | mv | mv thisfile.txt /home/thisdirectory |
| Lists files | dir | ls | ls |
| Clears screen | cls | clear | clear |
| Closes prompt window | exit | exit | exit |
| Displays or sets date | date | date | date |
| Deletes files | del | rm | rm thisfile.txt |
| "Echoes" output on the screen | echo | echo | echo this message |
| Edits files with simple text editor | edit | pico[a] | pico thisfile.txt |
| Compares the contents of files | fc | diff | diff file1 file2 |
| Finds a string of text in a file | find | grep | grep this word or phrase thisfile.txt |
| Formats a diskette | format a: (if diskette is in A:) | mke2fs (or mformat[b]) | /sbin/mke2fs /dev/fd0 (/dev/fd0 is the Linux equivalent of A:) |
| Displays command help | command /? | man[c] | man command |
| Creates a directory | mkdir | mkdir | mkdir directory |
| View a file | more | less[d] | less thisfile.txt |
| Renames a file | ren | mv | mv thisfile.txt thatfile.txt[e] |
| Displays your location in the file system | chdir | pwd | pwd |
| Changes directories with a specified path (absolute path) | cd pathname | cd pathname | cd /directory/directory |
| Changes directories with a relative path | cd .. | cd .. | cd .. |
| Displays the time | time | date | date |
| RAM and use | mem | free | free |
Basic Commands
Chang Password from GUI
To change your password using GNOME,
Go to System
Preferences
About Me
and then click Password.
Change the password the first time you log in
Change it regularly thereafter
Select a password that is hard to guess
Switching between virtual consoles and the graphical environment
A typical Linux system will run six virtual consoles and one graphical console
Server systems often have only virtual consoles
Desktops and workstations typically have both
Switch among virtual consoles by typing: Ctrl-Alt-F[1-6]
Access the graphical console by typing Ctrl- Alt-F7
Basic Principles of Linux and Unix
1. Open boot : OS is ready to display
Testing and initializing the hardware.
Giving you access to a set of tools to program and to debug it.
2. In Linux Everything is treated as files, including hardware devices : Every device has a file corresponding to it
3. It contains small single purpose programs
4. Ability to chain programs together to perform complex tasks
5. Avoid captive user interface : Limited number of user interfaces to manage OS/Applications
6. Configuration dataset stored in text format
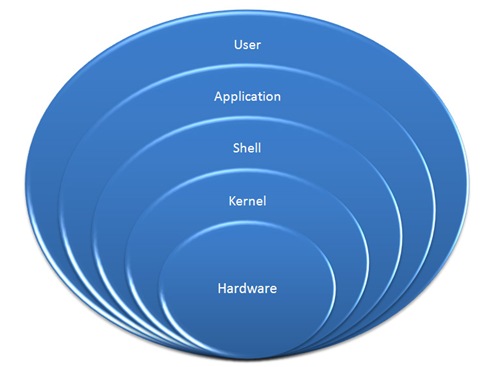
Operating system structure
the kernel is the central component of most computer operating systems; it is a bridge between applications and the actual data processing done at the hardware level.